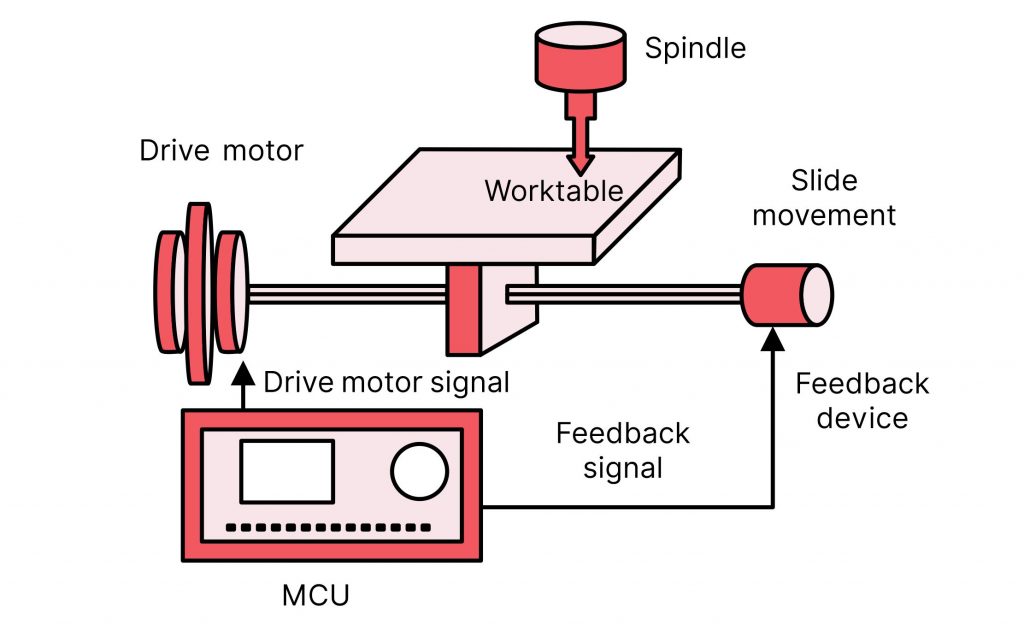
When talking about motor spindles and CNC in industrial automation, it is natural to think that speed is the important thing to emphasize. After all, a lot of industrial automation centers around large scale production who’s business model involves getting things made quickly. However, speed has proven to not be the sole factor in efficient production. Varying tasks requires different speeds to complete them. Furthermore, what speed works for one task does not necessarily work for another.
Read more: Unraveling Motor Spindle SpeedsVarying Speed Advantages
Today it is very commonplace for CNC machines to run varying speeds depending on what task needs completing. Different speeds come with different advantages when dealing with motor spindles completing specific jobs. As a result, CNC machines needs to have complete variable control.
Slow Speed
In applications where precision is paramount, low motor spindle speeds are often preferred. This is particularly true in industries like aerospace and medical manufacturing, where intricate parts require meticulous machining. Low speeds also, allow for precise material removal, reducing the risk of damage to delicate components. This is crucial in applications such as milling, drilling, and engraving.
Medium Speed
Medium spindle speeds find their place in applications that require a balance between precision and efficiency. Industries like automotive manufacturing often benefit from medium-speed machining processes. These speeds are suitable for a wide range of materials and can handle various cutting tools effectively. Medium speeds are commonly employed in generic tasks like turning, threading, and grinding.
High Speed
High-speed motor spindles are the driving force behind highly productive manufacturing processes. Industries focused on mass production, such as electronics and consumer goods, rely on high-speed machining for efficiency. Rapid material removal rates and reduced cycle times make high spindle speeds ideal for tasks like milling, drilling, and routing. The ability to process materials quickly without sacrificing quality is a key advantage in these applications.
The Need for Variable Speeds

Many modern CNC machines feature variable-speed motor spindles, allowing for dynamic adjustments based on specific requirements. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in environments where multiple materials or machining processes are involved. Variable speeds enable operators to optimize performance for different tasks within a single machining operation, enhancing overall efficiency and reducing setup times.
Motor spindle speeds also play a crucial role in managing heat generation during machining. In some applications, especially those involving hard materials, excessive heat can lead to tool wear and reduced tool life. Adjusting spindle speeds allows for better control over the heat generated during machining, promoting longer tool life and maintaining the integrity of the machined components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diverse motor spindle speeds available in industrial automation provide a spectrum of options for manufacturers to tailor their machining processes to specific needs. Understanding and effectively controlling motor spindle speeds are essential for optimizing manufacturing operations in industrial automation today. As technology advances, the integration of smart systems and real-time monitoring will further enhance the efficiency and adaptability of motor spindle speed control in industrial automation.
MRO Electric has a complete inventory of new motor spindles and VFDs. Please call 800-691-8511 or email sales@mroelectric.com for pricing and information. MRO Electric also offers repairs and replacement jobs.