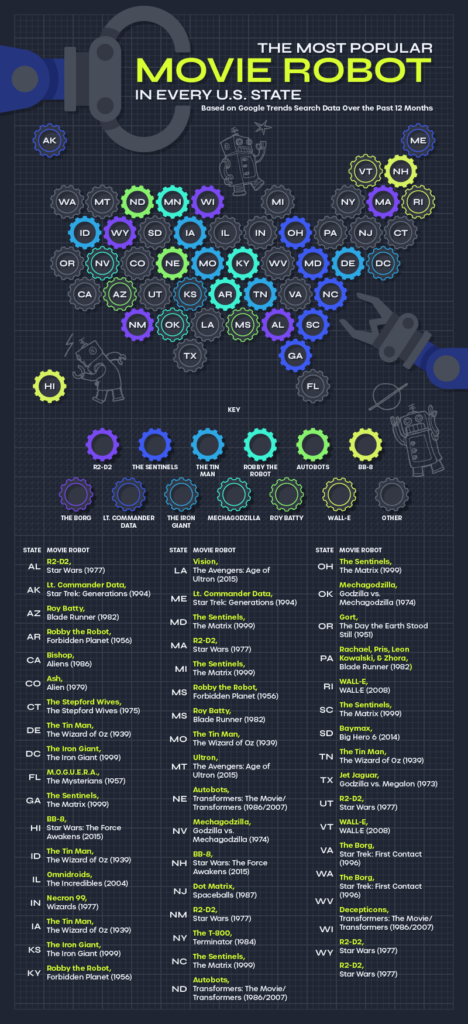
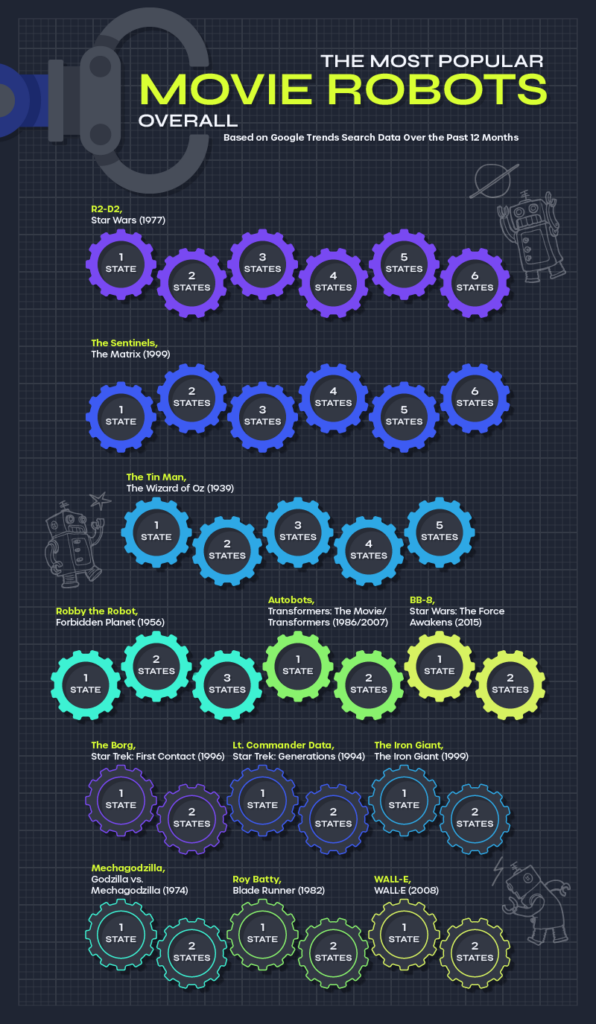
With no ceiling in sight for the climbing gas prices around the nation, many Americans are forced to adjust both their driving and spending habits to keep pace. Plus, with the holiday season in full swing, Americans need to account for higher airfare, food costs, and hotel prices as they plan their vacations, which may mean trips closer to home. Gone are the days of purchasing gas for under $2.00 per gallon. We now live in an era, where the price per gallon exceeds the federal minimum wage in certain locations––talk about pain at the pump.
Minimum wage workers and low-income commuters are suffering the most as a large percentage of their paychecks are being ravaged by rising gas prices. In California, a 12-gallon tank of gas costs minimum wage workers in some areas nearly 57% of a day’s pay. In some states like Pennsylvania and Utah, gas prices continue to rise, while minimum wage still sits at $7.25 an hour––where it’s sat for the last ten years, despite growing inflation rates.
To uncover where soaring gas prices are taking the biggest bite out of workers’ paychecks, MRO compared the minimum wage to the mean gas price in 100 U.S. cities. We dug deeper, focusing on 18 cities where gas costs over 80% of a minimum wage employee’s paycheck, ushering in a dystopian-like society all over the U.S. Read on to see where your city and state stack up.
What Causes Gas Prices to Go Up?
Low prices at the pump in our pre-pandemic world weren’t just a fever dream. If you remember, the demand for oil drastically fell during the pandemic as the world shut down and people were forced to stay home, but as the U.S. slowly started to recover, the demand for oil rebounded once more. The only problem? Oil production came to a grinding halt and drilling new oil wells takes a lot longer than ordering a new outfit through Amazon Prime. Plus, inflated energy prices, transportation costs, and a U.S. ban on purchasing oil from Russia all factor into soaring oil costs.
Why Is the Minimum Wage so Low?
The minimum wage was last raised thirteen years ago to $7.25 per hour on July 24, 2009, and it’s no secret that this amount has not kept up with inflation. Certain places like New York City have taken steps to raise the minimum wage for fast food workers to $15.00 per hour, but not every state and city has followed suit, leaving many wondering how they can survive and stretch their paychecks.
The minimum wage is indexed in 18 states and adjusts to keep up with inflation, but even this can vary depending on the individual counties within the same state. While President Biden did use executive order privileges to raise the minimum wage to $15.00 per hour for federal workers, republican and democratic lawmakers still can’t reach a resolution that satisfies either party’s agenda. With other pressing matters coming to a head, it’s not clear when or if a raised minimum wage that accounts for the rising cost of living will ever be ratified into law in the near future.
Can Minimum Wage Workers Afford the Gas Prices for Their Commute?

According to study results, minimum wage workers who make $5.15 per hour in Atlanta, GA pay $3.80 on average for a gallon of gas, resulting in 110.6% of a day’s paycheck being eaten by a full tank of gas (12 gallons). If the average commute in the U.S. requires 1.28 gallons of gas, then these Atlanta workers would lose wages just by showing up to work.
A full tank of gas consumes 93.1% of a day’s pay in cities like Boise City, ID, and it isn’t much better in places like Salt Lake City, UT, where 92.3% of a hard earned day’s wages is budgeted towards a full tank of gas. Those in Philadelphia, PA lose out on 85.9% of their paycheck towards a full tank. Minimum wage workers are stuck in a catch-22, but certain restaurant owners in Philadelphia are promising to raise their hourly wage to $15 per hour, creating light at the end of the tunnel.
Some customers are willing to pay higher menu prices to accommodate a living wage, and with the City of Brotherly Love welcoming 36.2 million visitors in 2021 alone, let’s hope this hot spot tourist destination can back these restaurant owners’ selfless initiatives.
Out of the top 18 cities where gas costs over 80% of a minimum wage worker’s paycheck, Pennsylvania holds five of those seats in places like Scranton (87.3% of a day’s pay), Pittsburgh (86.9% of a day’s pay), Harrisburg (86.4% of a day’s pay), and Allentown (85.5% of a day’s pay). The oil refinery explosion that occurred in South Philly in 2019 has forced the state to rely on imports more than ever before, contributing to the rising cost of gas.
Popular tourist destinations like New Orleans, LA, and Memphis, TN, are seeing skyrocketing gas prices at the pump. New Orleans minimum wage workers sacrifice 81.7% of a day’s pay to a gallon of gas while Memphis workers follow closely behind at 81.0%. Taking a trip to day drink at New Orleans’ historic bars? Avoid soaring gas prices and careen around the city on foot or with their bike share program.
The 5 States With the Largest Difference Between Minimum Wage and Average Gas Prices
Washington
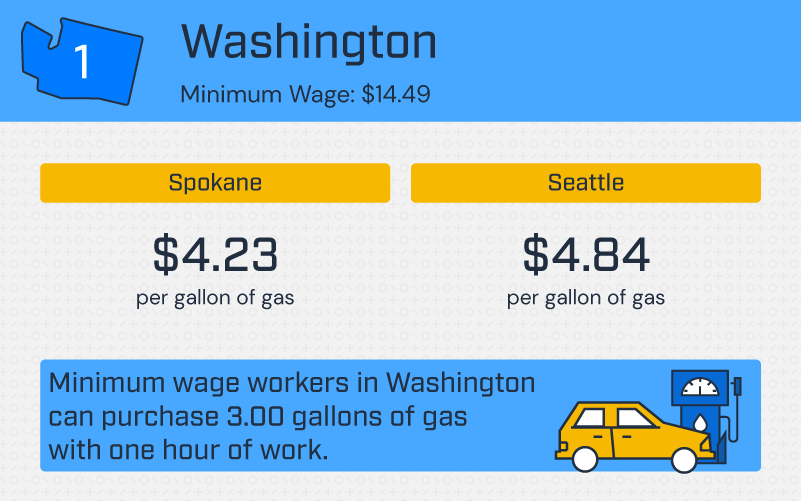
Next, we found the five states with the largest difference between minimum wage and average gas prices. Topping the list is Washington state. With a minimum wage of $14.49 and the average price per gallon of gas at $4.23, minimum wage workers in Spokane, WA can purchase 3.43 gallons of gas with one hour of work. Minimum wage workers in Seattle, WA can purchase 3.00 gallons of gas with one hour of work. What’s more, a full tank of gas (12 gallons) costs minimum wage workers in Seattle, WA 50.1% of their pay that day.
Massachusetts
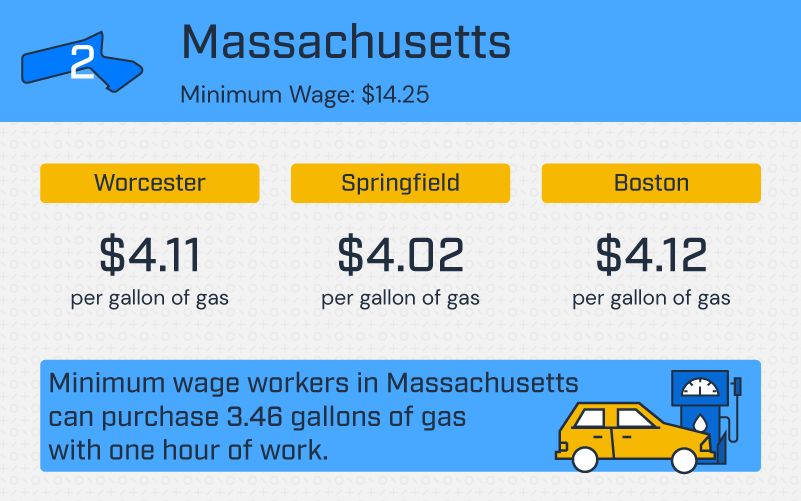
With a minimum wage of $14.25 and the average price per gallon of gas at $4.12, minimum wage workers in Boston, MA can purchase 3.46 gallons of gas with one hour of work. Additionally, a full tank of gas costs minimum wage workers in Boston, MA over 43% of a day’s pay.
Connecticut
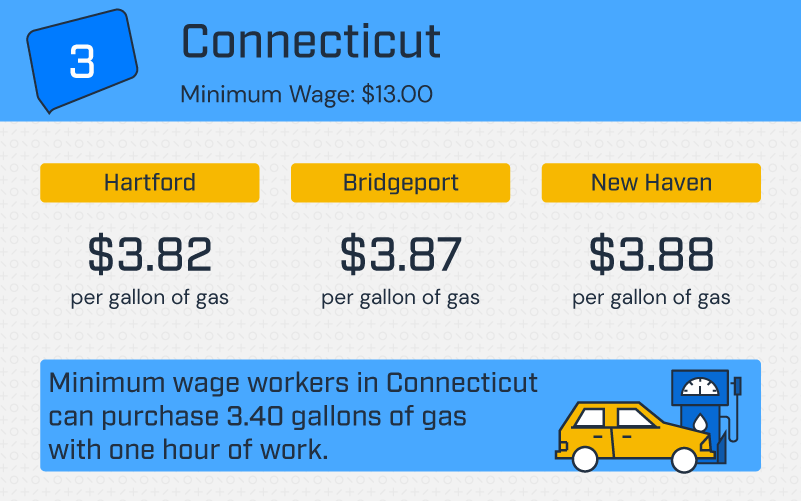
In Connecticut’s capital, Hartford, minimum wage workers can purchase 3.40 gallons of gas with one hour of work. In New Haven, CT, home of Yale University, that number drops to 3.35 gallons. Therefore, a full tank of gas costs minimum wage workers in Hartford and New Haven nearly 45% of a day’s pay.
New York

With a minimum wage of $13.20 and the average price per gallon of gas at $4.27, minimum wage workers in Rochester, New York can purchase 3.09 gallons of gas with one hour of work. Minimum wage workers in Buffalo, NY, and Albany, NY could purchase 3.13 and 3.17 gallons of gas, respectively.
Maryland

In Baltimore, MD, minimum wage workers can purchase 3.41 gallons of gas with one hour of work. Additionally, a full tank of gas costs minimum wage workers in Baltimore almost 44% of their pay that day.
Are There Any Signs of Relief on the Horizon for Minimum Wage Employees?
While minimum wage workers protest all over the country to get their voices heard, they still face an upward battle in this ongoing fight, despite there being a majority of Americans who are in favor of raising the minimum wage to $15.00 per hour. Governors in certain places like Pennsylvania are putting pressure on the General Assembly for a living wage and relief for their constituents. One survey found that while Republicans do agree the minimum wage should be increased, most would prefer raising it to $11.00 per hour, instead of $15.00. As states, cities, and local counties possess the authority to raise the minimum wage, this fight may need to be taken to the lower levels of power, instead of advocating for a living wage on a national scale, where it may find less success.
Gas Prices and Stagnant Minimum Wages Continue to Affect Consumers
That wraps up our study, comparing gas prices to minimum wage amounts around the U.S. Gas prices continue to be a dire issue across the country in 2022, as well as a harrowing expense for lower-income Americans who are also struggling to keep up with rising food prices and housing costs.
While MRO Electric can’t control the cost of gas, we can offer the parts and equipment you need to keep things getting from A to B. Get in touch with us today by emailing sales@mroelectric.com or calling us at 800-691-8511 for a quote.
Research Methodology
Using data from the U.S. Department of Labor and GasBuddy, we collected the minimum wage in each state and the mean gas price in 100 U.S. cities in April 2022. We divided the minimum wage in each state by the average gas price in each city to determine how much gas a minimum wage worker can purchase with one hour of work. For all minimum wage amounts by state, we collected the basic minimum rate per hour, as listed by the Department of Labor. Gas prices are always fluctuating, so prices may differ from the time frame the data was pulled.