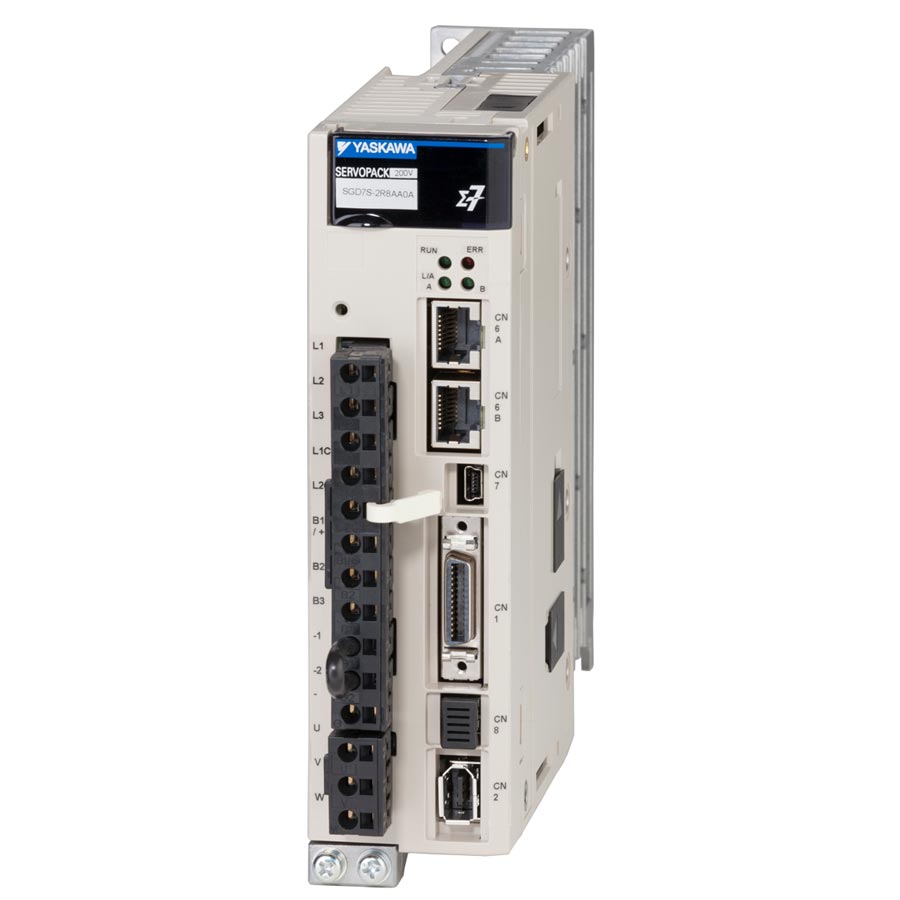
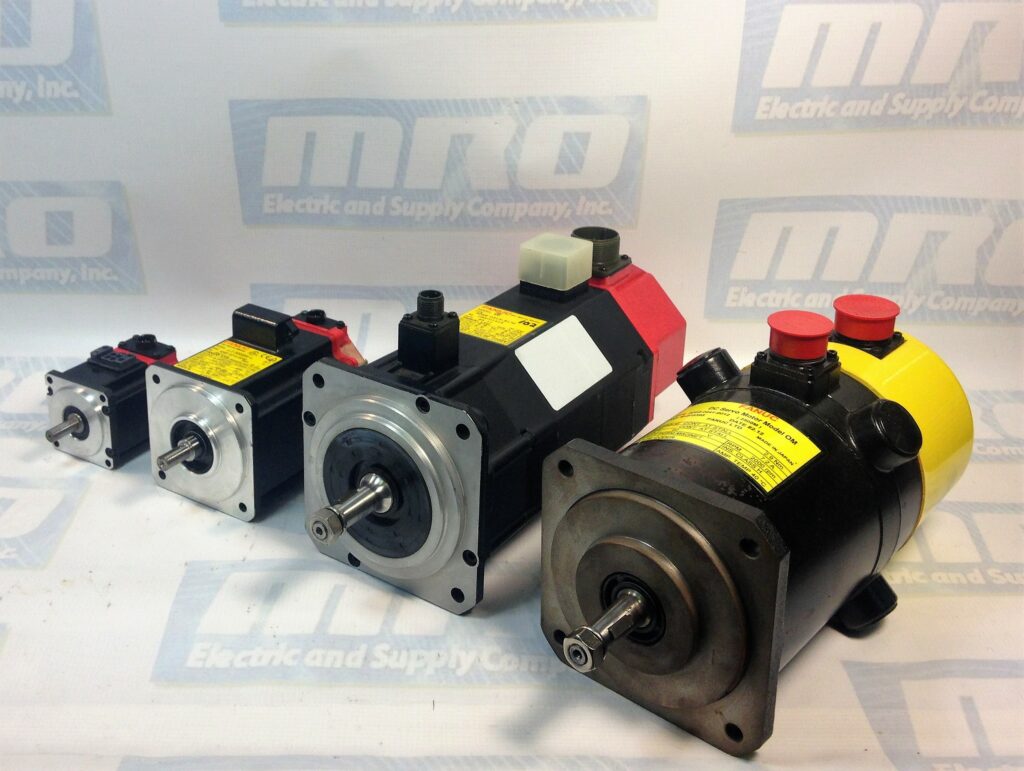
This year the most elite athletes from all over the world come together in Paris, France. There they will spend two weeks competing against one another in the Olympic games. It’s no secret that a lot of planning, work, and effort goes into the Olympics. While the spotlight understandably goes to the athletes and their coaches who compete. The success of the Olympics also hinges on its more technical side. When we talk about the importance of technical operations. Servo amplifiers in the Olympics are crucial componenst that can make or break an event..
Read more: Servo Amplifiers in the OlympicsServo amplifiers play an essential role in numerous applications within the Olympics. They ensure high precision, reliability, and performance across various sports and event operations. Here are some specific examples of how they are utilized:
Timing Systems
Timing systems like the ones made by Omega, the official time-keeping body of the Olympics, utilize servo amplifiers. Servo amplifiers control precision timing sensors and actuators, ensuring that the timing devices record the start and finish times to the thousandth of a second. This high level of accuracy plays an essential role in determining winners and setting new records. Track, Swimming, and Cycling are a few sports utilizing precision timing systems.
Robotic Cameras and Broadcast Equipment
Servo amplifiers play a big part when it comes to robotics, and the in the Olympics it is no different. Servo amplifiers offer precise and smooth motion for the camera to capture dynamic action from various angles without any shake or jitter. This precision control allows for cameras to pan and move while capturing fast-moving athletes as they make dynamic moves frequently missed by the human eye.
Gymnastics Equipment Calibration
When talking about gymnastics, factors like height, tension, and stability play very important roles in the outcome of gymnastics. Gymnastics requires everything to be precise and correct. This is not just limited to the actions and skill levels of the gymnast but also the equipment that they use. The slightest off set of height from a balancing beam or lack of tension on a line can cause an Olympian gymnast to lose their shot at the gold, if not something more catastrophic. The capability of servo amplifiers to adjust these factors with precise accuracy not only prevent unforeseen accidents, but also ensuring that someone takes home the gold!
Automated Training Simulators
High-end training simulators, such as rowing machines and treadmills used by athletes, often incorporate servo amplifiers. These amplifiers control the resistance and movement of the machines, providing athletes with consistent and precise feedback during their training sessions. For example, a rowing machine with a servo amplifier can accurately simulate the resistance of water, helping rowers to train more effectively.

Conclusion
Servo amplifiers are indispensable in the Olympic Games, providing the precision, reliability, and efficiency necessary for various applications. From timing systems and robotic cameras to training equipment and training systems, servo amplifiers enhance the overall performance and fairness of the competitions. As technology continues to advance, their role is set to become even more significant, contributing to the ever-evolving landscape of the Olympics.
Need a Servo Amplifier?
Have a tasks that requires peak levels of precision and functionality? Reach out to our team by phone: (800) 691-8511 or by email: sales@mroelectric.com. Check out our website www.mroelectric.com for more information on other products.