Servo motors are the unsung heroes of the modern technological landscape, silently powering everything from robots and drones to 3D printers and CNC machines. These miniature marvels are responsible for precise control and motion, making them indispensable in various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify the magic behind servo motors, explaining their operation, applications, and the intricate engineering that allows them to work their wonders.
Introduction to Servo Motors
At first glance, a servo motor may appear to be a simple, compact device. Still, beneath its unassuming exterior lies a sophisticated piece of engineering that combines precision, feedback control systems, and electrical circuits to deliver highly accurate rotational motion.
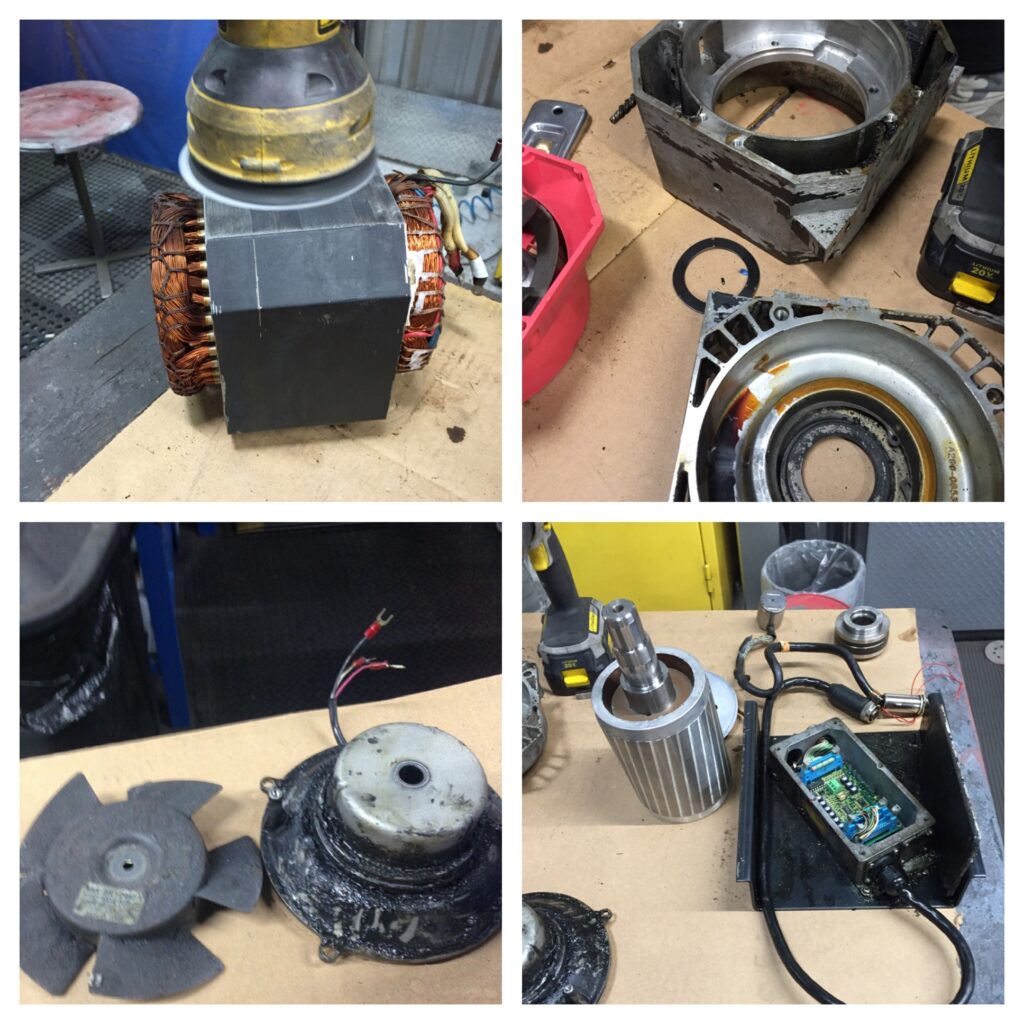

A servo motor typically consists of four main components:
- Motor: The heart of the servo, this component generates mechanical motion when electricity is applied.
- Feedback system: A sensor (usually a potentiometer or an encoder) that continuously monitors the motor’s position, allowing for real-time adjustments.
- Control circuit: The brain of the servo, responsible for processing feedback data and determining the required motor movement.
- Output shaft: This shaft extends from the motor and connects to the equipment or mechanism that requires precise motion.
Now, let’s dive into the inner workings of servo motors.
Read More